Application Portfolio Management (APM)
Application Portfolio Management is a discipline for the governance of software applications through their entire life-cycle in support of maximizing the business value delivered. APM thinking has four salient features:
- Governance Focus: The focus is on better IT decisions - higher business value at a lower cost, and risk
- Application Life Cycle: These decisions are along the entire application lifecycle - identify, select, fund, build, deploy, operate, and sunset
- Application Portfolio: The decisions are common across a group of applications.
- Application Categories: . in a category which contains applications with similar characteristics requiring similar governance approach
- Business Value: The objective is to govern the application portfolio driven by changing business needs for maximum business value
Application portfolio management (APM) is designed after the concepts of financial portfolio management. Application Portfolio Management is also referred to as Application Portfolio Rationalization. [1]
The concept of application portfolio management (APM) first emerged in the early 1990s, but its benefits really became apparent during the Y2K buildup. When organizations began preparing for Y2K remediation, they often discovered they had accumulated a large number of applications that were redundant, costly to maintain, and of little real business value. Moreover, the majority of applications were not cataloged in any logical, searchable fashion. As companies began to review their application portfolios, the benefits of having an ongoing process of doing so became apparent. For example, IBM claims it was able to reduce the number of its application systems from 15,000 in 1998 to 6,800 in 2000, following a companywide effort to optimize its portfolio. The applications in most of these organizations were not cataloged in an easy and search-friendly manner. This meant that there was a need for reviewing the application portfolios. Also, businesses obtained a clear idea of the advantages they could derive from these applications. [2]
Requirements of Application Portfolio Management [3]
There are three facets involved in application portfolio management. These include grouping, governing, and management tools.
- Grouping is perhaps the most important function involved in application portfolio management. In this scenario, applications that include similar functions are assessed according to their financial values and cataloged in a way that makes it easy to analyze them at a later period at multiple levels.
- APM also needs to incorporate an ongoing process to ensure that all future developments that include upgrades and other fixes or changes in the application are recorded. This is the governance part of application portfolio management where the processes are implemented at the same time when applications are rationalized and this ensures that the entire process is effective.
- The next essential factor is an APM system which helps automate the process and provides the CIO with an overview of the value, risk, and the number of applications that are present within an organization. These tools also provide a closer look at each of the groups within an organization and enable the IT infrastructure of an organization to be aligned closely with priorities such as budget as well as other business strategies.
Application Portfolio Management Lifecycle [4]
Application portfolio assessment, if carried out in a balanced fashion, can be of immense value before a modernization initiative and approach are finalized. It brings clarity on where most value risk anomalies are and how to objectively prioritize and create a modernization sequence to effectively address business and IT concerns. Let us look at the reasons why it happens – after all the stakeholders strive for these initiatives to succeed.
- The first major reason is that significantly few organizations know the real ‘as-is state’ of their application portfolio. At a strategic and operating level, there are visible, mostly aggregated symptoms of the problems, but nobody ever gets the priority and time to objectively break it down at the application level. It is like having a map, knowing where you want to be but without that “you are here” point on the map so you cannot work out your route options (traffic conditions, weather), budget, and timelines. In the context of an application portfolio this “you are here” point is determined by several factors such as Total Cost of Ownership, value and risk of an application in the strategic and operating continuum, operating model for IT development and support, and degree of alignment between business and IT strategy.
- The second reason is the lack of or inadequate portfolio governance in various degrees and dimensions. Application Portfolio Management (APM) can effectively address these deficit areas. Lack of or insufficient portfolio governance creates value risk anomalies and complexities, multiple sources of truth for portfolio information, and severely limits the ability to quickly respond to business needs.
APM is a strategic IT management approach for managing risks and costs of IT assets to maximize their value to the business. It provides a management framework to support a continuous process of portfolio optimization covering the complete IT investment lifecycle (refer to the image below) where it starts with strategic objectives and business priorities driving the portfolio assessment recommendations which, when integrated with the budgeting process, leads to the right portfolio priorities and their most effective execution sequence.
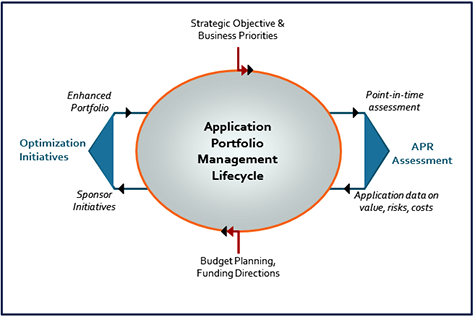
source: NTT Data
Another factor is the view that major stakeholders maintain toward their business applications portfolio. This view, to a large extent, influences how and at what level portfolio-related issues are articulated and addressed (i.e., a technology problem, an IT operations problem, or a business problem). A mature portfolio assessment and rationalization approach establishes a single source of truth in your applications portfolio, providing insights that help you rebalance your IT assets to optimize the value-risk and cost equation.
The Process of Application Portfolio Management [5]
A four-step process is illustrated in the figure below:
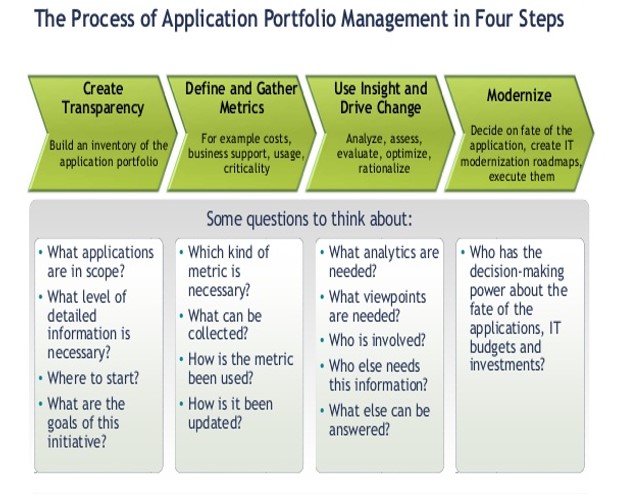
source: SoftwareAG
Benefits of Application Portfolio Management [6]
Application portfolio management involves continuous assessment of the application portfolio in terms of business value, enhancement potential, cost, and technology concerns. Such comprehensive evaluations help facilitate strategic application development, maintenance, transformation, and retirement, which, in turn, can help companies:
- Align the application portfolio with business strategies
- Develop Enterprise Applications: APM can assist IT in planning enterprise applications that replace many smaller applications that sit in silos and inhibit the enterprise's ability to gain a single view of a customer or constituent. A clear picture of the limitations of applications in the portfolio can identify opportunities for system development that transform business and create efficiencies where they previously did not exist.
- Reduce costs and optimize value:
- Application Development Cost Reductions: A closer analysis of the components of each of the applications in the portfolio allows IT to leverage more application code when developing a new application.
- Elimination of Redundant Applications: Because applications were created in silos over the years, many applications essentially perform the same functions as other applications. Applications can be consolidated and applications that are no longer needed can be sunset. This saves money and reduces the costs of system maintenance and enhancements.
- Elimination of Applications of Little or No Value: Applications that are returning little or no value to the business can be eliminated.
- Shared Services and Applications: Knowledge of the portfolio allows sharing services instead of building or procuring them in some cases. When a new service is requested IT can examine the portfolio to determine whether a solution to the need already exists. If so, that application can be shared or copied.
See Also
- Application Lifecycle Management (ALM): ALM manages the end-to-end life cycle of an application from conception through retirement. APM often intersects with ALM, as managing the portfolio effectively requires understanding each application's stage in its lifecycle.
- IT Portfolio Management (ITPM): While APM focuses specifically on applications, IT Portfolio Management takes a broader view, encompassing all IT investments, including hardware, projects, and other resources. APM can be considered a subset or specialized form of IT Portfolio Management.
- Enterprise Architecture (EA) : EA involves designing the structures and behaviors of an organization's enterprise systems. APM supports EA by providing a clear view of all applications in the organization, aiding in alignment with business goals and strategies.
- IT Governance: IT Governance provides a structured framework for aligning IT strategy with business goals. APM plays a key role within this governance, ensuring that application investments are aligned with organizational objectives.
- IT Service Management (ITSM): ITSM focuses on delivering and supporting IT services. APM interfaces with ITSM by helping determine which applications need to be serviced, upgraded, or retired based on their business value and relevance.
- Software Asset Management (SAM): SAM is a business practice that involves managing and optimizing software applications' purchase, deployment, maintenance, utilization, and disposal. APM overlaps with SAM in areas concerning the evaluation and management of software assets.
- Cloud Computing: As organizations migrate applications to the cloud, APM aids in deciding which applications to retain, retire, or refactor for the cloud environment.
- Technology Roadmapping: Technology road mapping is about planning the integration and development of technological solutions. APM informs this process by offering insights into the current application landscape and future needs.
- Business Process Management (BPM): BPM focuses on improving corporate performance by managing and optimizing company business processes. APM can inform BPM by offering insights into which applications support which business processes and how effectively they do so.
- Change Management: Change Management introduces and implements organizational change. APM plays a role in this when applications in the portfolio undergo transitions, upgrades, or retirements.
References
- ↑What is Application Portfolio Management?
- ↑Computer The Origins of Application Portfolio Management (APM)
- ↑The Facets of Application Portfolio Management
- ↑Application Portfolio Management Lifecycle
- ↑The Process of Application Portfolio Management
- ↑What are the Benefits of Application Portfolio Management?
Further Reading
- How Application Portfolio Management and Enterprise Architecture Add Up to IT Governance
- Turn Application Portfolio Management into a Governance Tool for the CIO: A pragmatic approach to manage optimization and transformation of your application portfolio



